565,225 electric bicycles were sold in France in 2024 (38,000 in 2012), all of which had in common being equipped with lithium-ion batteries. In 10 years, this technology has established itself as the norm.
However, the press and firefighters regularly report cases of explosions or fires related to lithium-ion batteries.
The cause? A phenomenon called thermal runaway, triggered by problems with quality, charging, or impacts, among other things.
Where are the fires taking place in France?
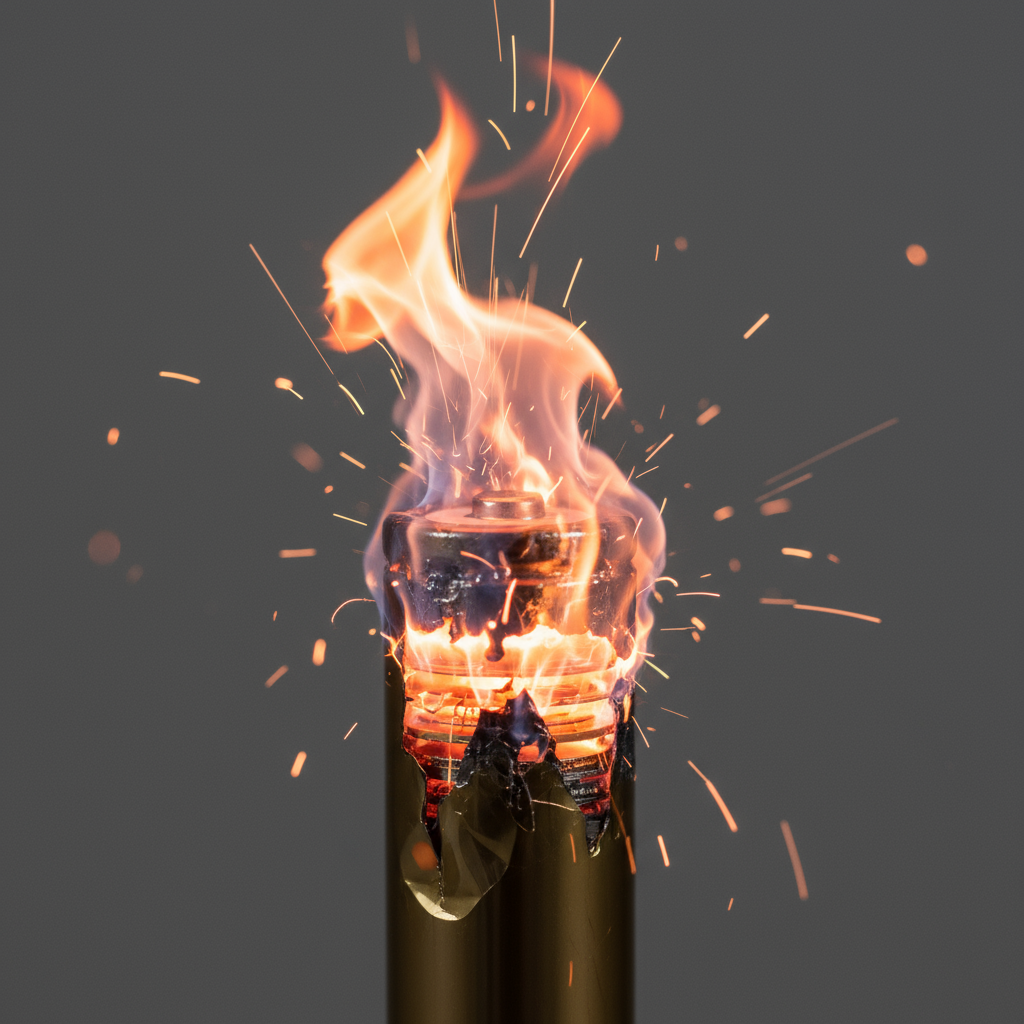

Thermal runaway
Falls, short circuits, crushing, overload: 4 common situations are enough to trigger a fire.
When damaged or overloaded, they can undergo thermal runaway: the cell heats up uncontrollably, releases oxygen, and ignites the electrolyte.
This phenomenon is self-sustaining: a cell on fire transmits its heat to neighboring cells, triggering a chain reaction. The result: flames reaching several hundred degrees, toxic fumes, and sometimes explosions.
This explains why a simple handling accident or an improperly supervised recharge can cause a significant fire, both in an apartment and in a storage warehouse.
What good habits should you adopt?
Always use an undamaged battery.
- Never use a battery that has been impacted or deformed. If a battery has fallen from more than one meter or has been involved in an accident, do not use the battery for at least 48 hours and keep it under surveillance.
- If you are unsure about the history of a battery (used, second-hand electric bike), it is strongly recommended not to use it.
Always remain vigilant during charging.
- Never leave it charging unattended, especially at night or when you leave your home.
- Do not leave a battery plugged in once charging is complete: unplug it to avoid any risk of overcharging.
- Always use the charger and cables provided or approved by the manufacturer to ensure safe charging.
Always charge your lithium-ion battery in a safe place.
- Never charge your battery in a location that blocks an escape route or the only exit from your home. In the event of a fire, this mistake can make evacuation impossible.
- Always place the battery on a hard, non-flammable surface such as tile or concrete when charging, and avoid sensitive materials such as parquet flooring, carpets, or a sofa.
Protect the battery from extreme temperatures and humidity.
- Below 5°C, the battery loses capacity and becomes more unstable: wait for the device to warm up before starting a charge.
- Avoid any exposure to direct heat (sun, radiator, flammable surface) which promotes overheating.
- Avoid moisture, which can damage the internal circuits.
What to do in case of fire?
- Never use water: Water should be avoided as it can worsen the fire by causing a short circuit. Use only a powder or CO₂ extinguisher , or failing that, cover the battery with sand.
- Always secure the premises: Evacuate people immediately, ventilate the room if possible, move flammable materials away, and call for help without delay.
- Never handle the battery: Do not touch the battery, even once the flames are extinguished, as the internal heat may persist and reignite the combustion.